Treatment And Recommendations In Solar Erythema
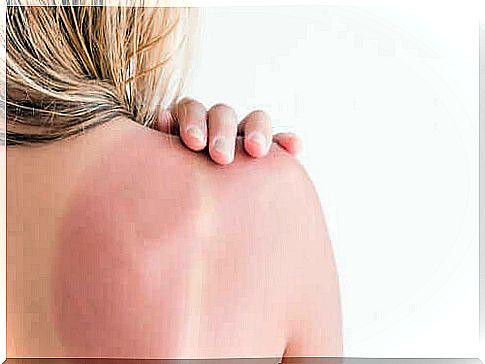
Today we are going to talk about the treatment and recommendations in solar erythema. Solar erythema is the typical sunburn you get when you are exposed to ultraviolet radiation for a long time. In general, the most intense symptoms appear in the first 24 hours and then begin to subside.
What is known as solar erythema is a range of conditions with varying degrees of severity. There are mild lesions, with only a peeling of the outer layer of the epidermis.
Other times, however, the burn causes excoriation and blisters. In either situation , the affected area turns red from blood congestion. There is not always inflammation, but the flow of fluid into the tissues can increase in volume.
As we mentioned, solar erythema comes from the ultraviolet rays of the sun. Although there are different wavelengths in the sun’s rays, the radiation that affects the skin the most is UVB and UVA.
UVA radiation is very penetrating and can reach the subcutaneous tissue, which is located under the epidermis. The negative effects of this type of radiation manifest themselves in the long term. It accelerates cell aging and promotes the development of skin cancer.
In addition, UVB radiation is the direct cause of solar erythema or sunburn. The skin discolors and burns due to this radiation. It is also capable of altering cells and making them malignant. Both radiations are therefore a risk factor for cancer.
High-risk groups for solar erythema
Anyone can suffer from solar erythema if they expose themselves too much to the sun’s radiation at times when the sun is stronger and unprotected. In any case, certain population groups are more susceptible to these burns. Among them are:
- Those who have to work outside around noon.
- People with a very light skin color.
- Those who practice water sports or mountain sports, as the reflection of the water and snow is able to burn with the same intensity as direct light.
- Inhabitants of the tropics, where the direction of the sun is more perpendicular to the earth and the radiation schedule is longer.
- P atiënten using certain antibiotics, such as doxycycline.
- Chronic patients with autoimmune diseases in which the skin is affected, such as lupus (Spanish link).
Recommendations for if you have solar erythema

Once you have solar erythema, you need to take steps to alleviate the injury. In these cases, you usually don’t need to see a doctor. However, if you are in any doubt about the severity or development of the burn, we recommend that you consult your doctor.
If you know that you have been exposed to the sun a lot and that the erythema will certainly occur, then you should shower with lukewarm/cold water when you get home. You can also place cold objects on the affected skin to control the inflammation that will appear.
You should wear loose-fitting clothing as long as the erythema is present. The friction of shirts and pants hurts, in addition to promoting flaking, which can be dangerous if there are blisters.
If you have fluid-filled blisters, don’t break them. You have to let them develop without too much intervention. You can rub creams with painkillers and coolants around them and cover them with a sterile bandage so they don’t get infected.
As for medication, the article “Approaching the treatment of skin aging” in the journal Ars Pharmaceutica (Spanish link) suggests the use of gotu kola in creams. This can stimulate the production of collagen to repair the skin. Orally you can use paracetamol to control the pain.
Take care of yourself by using sunscreen

We recommend using sunblock with at least 30 SPF. Sunscreen is a fundamental tool in summer and all year round. Dermatological associations recommend using it in direct sun exposure and especially in high-risk groups.
What sunscreen does is reflect or absorb radiation to prevent it from reaching the skin. The unit of measure used for these creams is the sun protection factor (SPF). Each SPF is associated with a percentage of UV radiation filtration.
In practice , a sunscreen with SPF 30 is sufficient in most cases, as it blocks 96.7% of the radiation. Using a higher factor is useful for your face, for children or people with very light skin tones.
However, it is important to know how to apply and maintain it. To avoid sunburn, spread the cream evenly over your body, creating a layer of at least 2 milligrams per square inch of skin.
Protecting yourself from solar erythema is one of the recommendations
While it may not seem like it, protecting yourself from solar radiation is a habit that affects your future. You can prevent most cases of skin cancer if you take at least the minimum measures to avoid sun exposure and use enough sunscreen.
When in doubt about a skin injury, be it solar erythema or a more severe burn, one of our recommendations is to see a doctor. It is best to follow their advice on the severity of the condition and act accordingly.