The Differences Between Odynophagia And Dysphagia

Odynophagia and dysphagia refer to a range of problems related to food intake. However, these two concepts have some differences that we will discuss in this article today.
Despite the fact that many people confuse both terms, the truth is that if you learn more about them, you will realize how different odynophagia and dysphagia are, despite the fact that they are also related to each other.
What is odynophagia?
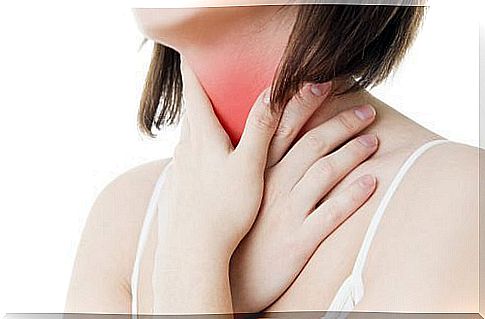
First of all, we discuss the concept of odynophagia. As the study rightly points out gastroesophageal reflux disease (Spanish link), it refers to the pain that occurs when people swallow (solid foods, liquids, or saliva). Some of the features are:
- Mild pain. While it can increase in some circumstances, it is usually quite mild.
- Chronicity. In some cases, the pain during swallowing becomes chronic, which may indicate a serious illness that needs to be treated.
- Synchronous contractions. The muscles in the area contract and cause pain.
Causes
Odynophagia usually manifests as a result of diseases such as strep throat, tonsillitis or other infections that can affect the throat area. However, once the cause of the odynophagia is gone, it disappears.
This does not happen in other situations, where this painful swallowing becomes chronic. It can be a warning of a major problem. For example, a stomach ulcer.
However, if you are concerned about all this in vain, then if you have any of the symptoms listed above, you should see your doctor to rule out any problems. You can also start an appropriate treatment in this way to solve the problem.
What is Dysphagia?
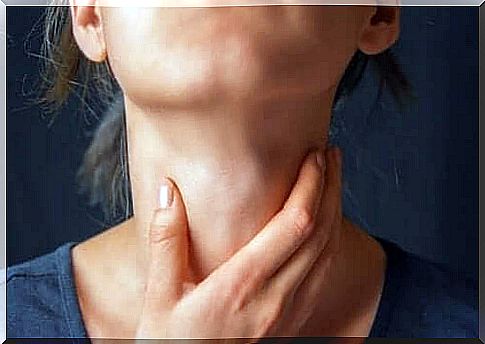
Now that you know a little more about odynophagia, let’s talk about dysphagia. In this case, dysphagia is difficulty swallowing both solid and liquid foods (Spanish link).
In fact, foods stop their journey before they reach the throat because they can’t get through it. Sometimes patients with dysphagia may have difficulty chewing food, which is commonly referred to as a “ball” or “bolus.” Some of the symptoms of dysphagia coincide with those of odynophagia:
- Pain on swallowing (odynophagia). This is why food or liquids cannot make their normal journey.
- Globus sensation. This is a symptom of anxiety characterized by the feeling of stiff and tight throat muscles, causing the throat to narrow.
- Hoarseness. This is due to the contraction of the muscles in the area.
- belching. The inability to swallow causes food to return to the mouth. So it doesn’t go down the throat.
- Gag reflex. Because of the swallowing problems and the belching that causes dysphagia.
Causes
Some of the causes of dysphagia include achalasia (a rare disease that affects the esophagus), inflammation of the esophagus (which may be related to a food allergy), or the presence of tumors in the area.
If you go to your doctor with these symptoms, the first thing they will do is check that there are no foreign objects causing the dysphagia. In some situations, a piece of food can be the cause of this annoying problem.
How to prevent odynophagia and dysphagia
Now that you’ve seen the differences between odynophagia and dysphagia, even though one is a symptom of the other, it’s important to know how to prevent them.
Experts recommend chewing food well and avoiding excessive amounts of foods that are difficult to swallow. You should also have good habits for staying as healthy as possible and avoiding strep throat or other infections that can cause this condition.
Finally , don’t forget the importance of seeing your doctor regularly to make sure everything is okay. Early detection of a stomach ulcer, gastroesophageal reflux disease or cancer can ensure that you will not suffer from odynophagia and dysphagia for a long time.