Food Additives: Allergies, Symptoms And Treatments

An allergy to food additives is a problem that often goes undiagnosed because people can mistake it for a food intolerance. However, these are different phenomena, even though both have a common origin and similar symptoms.
When it comes to food intolerance, complaints arise because the person has difficulty assimilating a food or food additive properly. The immune system is not involved in this.
With regard to allergies to food additives and to food in general, the immune system reacts disproportionately to them. This can be life-threatening in some severe cases.
The population generally pays more attention to food intolerances or food allergies than to allergies to food additives.
This is because the latter are present in most ultra-processed foods and those who consume them often ignore their harmful potential.
Food additives
Food additives are substances that are added to certain foods during processing. They have properties that are used to influence the product, including in the areas of:
- taste
- texture
- colour
- aroma
- shelf life
Manufacturers add these substances with approval from the FDA or other national health authorities and usually list them on the product label. The rules for this are determined per country.
An allergy to food additives occurs when the body identifies them as potentially dangerous. So it triggers an immune response to attack the substance with symptoms that can range from mild to very severe.
Symptoms of Allergies to Food Additives
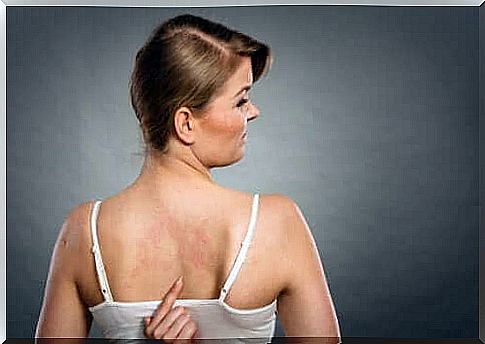
The symptoms of an allergy to food additives can vary widely. Allergies to food additives usually cause respiratory or skin complaints.
- The most common are respiratory complaints, especially asthma and rhinitis, but also the skin.
- Problems such as hives and other forms of dermatitis usually develop.
However, the symptoms can also progress and cause a severe reaction called anaphylaxis, which is life-threatening. This happens quickly and violently and it is due to the enormous release of, among other things, histamine. It also narrows the airways and can lead to death.
Currently, researchers believe that between 5 and 10% of chronic hives are due to allergies to food additives. However, the figure could be higher but evidence for this is lacking.
In fact, there are currently several limitations in diagnosing this problem. In general, however, the appearance of complaints after eating certain foods can be a signal that an allergist should assess.
The potential risk of some food additives
All food additives can cause side effects, but some have an even higher potential risk. These include the following additives:
- Industrial antioxidants. Doctors report cases of hives and atopic dermatitis as a result of ingesting foods containing industrial antioxidants. In some cases, it produces bronchospasm.
- Sulfur dioxide and sulfites. The latter can cause respiratory symptoms such as rhinitis or aggravation in asthmatics. They can also lead to dermatitis, hives and digestive problems.
- Nitrates and nitrites. These can aggravate atopic dermatitis and, in addition, lead to cases of severe allergic reactions.
- Benzoic acid and benzoates. These are the most common additives in allergic reactions. They aggravate atopic dermatitis and asthma, hives, headaches, migraines, difficulty concentrating and hyperactivity.
- Methylcellulose. This additive may lead to adverse gastrointestinal reactions.
- E441. It is a thickening agent that can cause severe allergic reactions in people who are allergic to it.
- Guar gum and tragacanth gum. The former can cause gastrointestinal problems. The latter can aggravate atopic dermatitis or cause hives.
- Monosodium glutamate. This product may cause serious allergic reactions.
- Dyes. They can cause mild, moderate or, in rare cases, severe allergic reactions.
Treatments

So to control allergies to food additives, you should avoid the processed foods that contain them. Instead, opt for fresh, natural foods that are also free of pesticides.
There is no effective cure for these types of allergies. The only option is to eliminate them from your diet. This can be quite difficult at times as there are many foods with additives on the market.
It is complicated because additives are not always listed by name, but by reference number. It is important to research the name of the components that correspond to a number or code that appears on a food label.
The best measure then is to avoid prepackaged ultra-processed foods, especially those of industrial origin. The less industrially processed a food is, the fewer additives it will contain.
The best diet for people with allergies to certain additives is therefore the diet where you only eat fresh and natural ingredients. In addition, you should avoid consuming foods whose ingredients are unclear. We recommend that you simply do not try them in such cases.